Immersive stadiums: The audiovisual revolution redefining the fan experience
The digital transformation of the audiovisual industry has brought about a radical shift in how audiences consume content at large-scale events, from sporting fixtures to concerts. This phenomenon is especially evident in what we now refer to as immersive stadiums: venues that combine advanced audiovisual technologies to create sensorial and emotional experiences capable of completely transforming the attendee’s perception.
The technological leap from the traditional stadium to the immersive stadium
Historically, attending a live event meant an experience limited by physical distance, the venue’s acoustic quality, and the visual perspective from one’s allocated seat. In recent years, technologies such as Extended Reality (XR), spatial audio systems, and panoramic LED displays have made a powerful entrance, triggering a technical revolution that turns stadiums into environments that break the barrier between spectator and spectacle.
In these new venues, the audiovisual experience becomes the core of the design. Attendees no longer simply witness the event—they are actively immersed in it, becoming emotionally and sensorially integrated into every key moment of the experience.
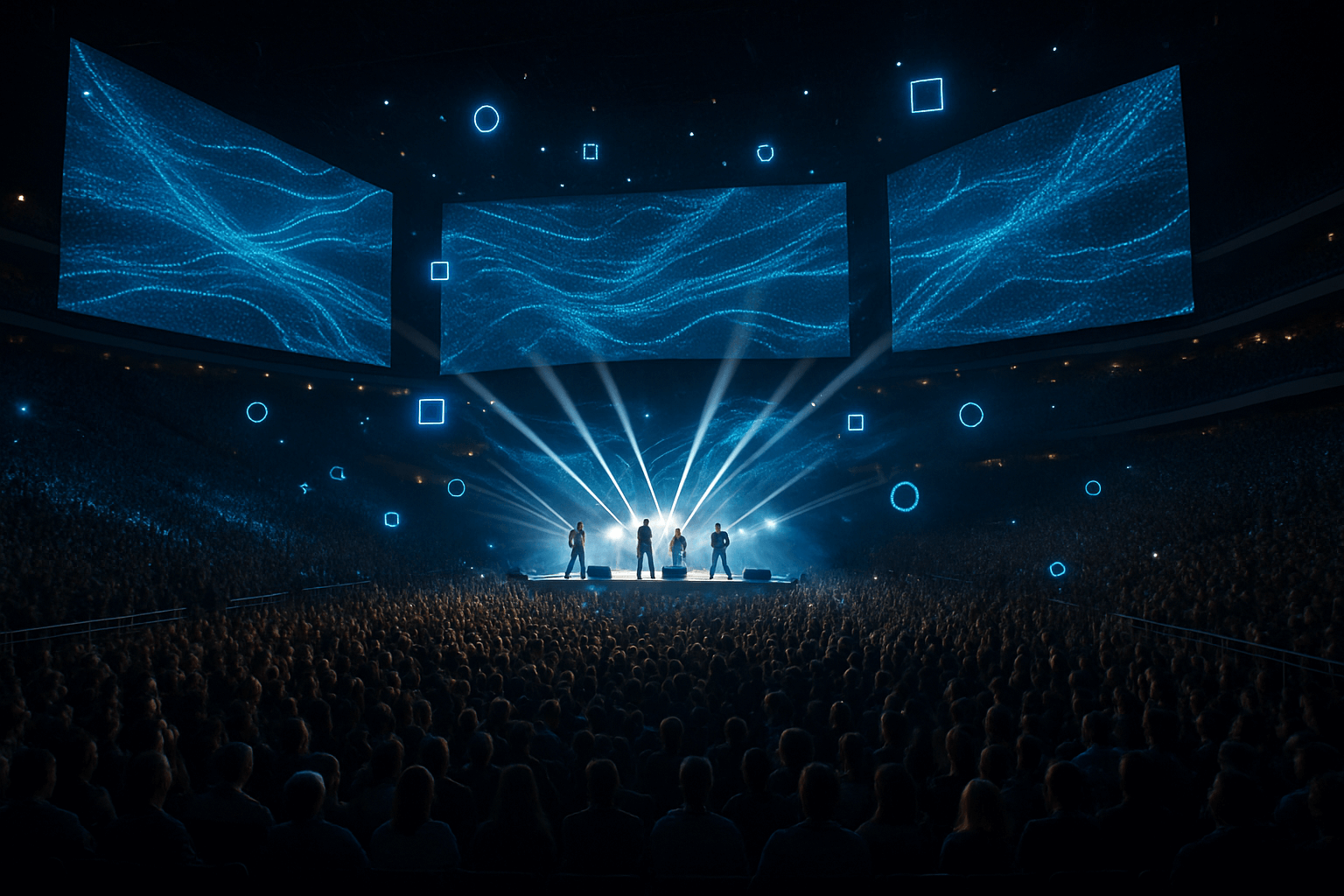
Key components of the immersive stadium
Surround LED screens
Immersive stadiums employ vast LED screens that fully surround the audience. These screens go beyond showing replays or the scoreboard—they integrate enriched content such as real-time dynamic graphics, advanced statistics, and interactive animations, significantly enhancing understanding and enjoyment of the event.
Spatial sound systems
Installing spatial sound systems allows spectators to experience sound events with exceptional clarity and positional accuracy. Achieved through complex networks of distributed speakers and digital audio processors, these systems produce a three-dimensional soundscape. A football fan, for example, can follow the movement of the ball across the pitch, or a concertgoer can feel a musical note travelling through the stadium.
Augmented Reality (AR) and mobile applications
Integrating mobile apps with augmented reality is another cornerstone. Through smartphones and tablets, spectators can access live augmented information about the event: player stats, performance data, historical narratives, or background on performing artists. This technology enhances the depth and interactivity of the live experience.
Haptic and multisensory seating
The inclusion of haptic seating is a major breakthrough. These seats deliver vibrations synchronised with key moments—goals, standout plays, or dramatic musical climaxes. This tactile layer is often accompanied by additional effects such as scents, mist, and temperature changes, contributing to a fully immersive, multi-sensory experience.
Practical applications across event types
Sporting events
At sporting events, immersive tech significantly enriches the fan experience with live statistics, multi-angle replays, and interactive graphics. This not only boosts entertainment but also enhances the audience’s understanding of the game.
Concerts and live shows
In concerts, immersive audiovisual technologies allow performers to build interactive digital sets that react in real time to the music, the crowd, or the artist. Large-scale LED displays, architectural projection mapping, and sensory effects create unforgettable atmospheres, increasing both emotional and artistic impact.
E-sports and gaming events
E-sports, one of the fastest-growing entertainment sectors, make particularly strong use of these technologies. Cylindrical LED screens and fully immersive AV systems transport the audience into the game itself, offering a complete and dynamic view of the virtual battlefield.
Technical challenges and current solutions
Creating an immersive stadium involves several technical challenges that the industry is actively addressing:
- Latency and synchronisation: Audio and video must be synchronised with less than 10 milliseconds of delay to ensure seamless audiovisual perception. Hybrid private networks (fibre optics and private 5G) and edge computing help achieve this.
- Interoperability: The integration of multiple systems—spatial audio, LED screens, AR—requires standardised protocols to ensure smooth, continuous information flow.
- Scalability and robustness: As events differ in size and technical demands, solutions must be adaptable and scalable, while consistently delivering high-quality standards.
Future trends and technological Outlook
Technological advancement continues. Key trends shaping the next generation of immersive stadiums include:
- Collective virtual reality: The use of VR headsets in the stands to offer complementary and personalised experiences.
- Predictive Artificial Intelligence: Algorithms that adjust the audiovisual narrative in real time based on individual audience preferences, using behavioural data to tailor the experience.
- Holographic technology: Live holographic projection of artists, athletes, or key figures, enhancing the blend of digital and physical presence.
The shift from traditional to immersive stadiums is redefining what it means to attend a live event. The power of audiovisual technology not only amplifies the sensory experience but sets a new benchmark in entertainment, where the spectator becomes an active part of the story.
For AV operators and system integrators, adapting to this new reality means developing robust, flexible solutions that can meet growing demand and evolve at the rapid pace of innovation.
The era of immersive stadiums is already upon us—radically changing how we experience, feel, and participate in large-scale events.
Asier Anitua Valluerca
Gerente Desarrollo de Negocio
Telefónica Servicios Audiovisuales
